
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Electromagnetics and Acoustics and Department of Physics, College of Physical Science and Technology, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117583, Singapore
3 School of Physical Science and Technology and Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Thin Films, Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, China
Vortex waves with orbital angular momentum (OAM) are a highly active research topic in various fields. In this paper, we design and investigate cylindrical metagratings (CMs) with an even number of unit cells that can efficiently achieve vortex localization and specific OAM selective conversion. The multifunctional manipulation of vortex waves and the new OAM conservation law have further been confirmed through analytical calculations and numerical simulations. In addition, we qualitatively and quantitatively determine the OAM range for vortex localization and the OAM value of vortex selective conversion and also explore the stability for performance and potential applications of the designed structure. This work holds potential applications in particle manipulation and optical communication.
vortex waves cylindrical metagratings vortex localization high-efficiency transmission vortex selective conversion Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 033601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Xiamen University, Institute of Electromagnetics and Acoustics, College of Physical Science and Technology, Department of Physics, Xiamen, China
Hyperbolic shear polaritons (HShPs) emerge with widespread attention as a class of polariton modes with broken symmetry due to shear lattices. We find a mechanism of generating quasi-HShPs(q-HShPs). When utilizing vortex waves as excitation sources of hyperbolic materials without off-diagonal elements, q-HShPs will appear. In addition, these asymmetric q-HShPs can be recovered as symmetric modes away from the source, with a critical transition mode between the left-skewed and right-skewed q-HShPs, via tuning the magnitude of the off-diagonal imaginary component and controlling the topological charge of the vortex source. It is worth mentioning that we explore the influence of parity of topological charges on the field distribution and demonstrate these exotic phenomena from numerical and analytical perspectives. Our results will promote opportunities for both q-HShPs and vortex waves, widening the horizon for various hyperbolic materials based on vortex sources and offering a degree of freedom to control various kinds of polaritons.
hyperbolic shear polaritons vortex waves off-diagonal imaginary component scaling factor topological charge Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(1): 015001
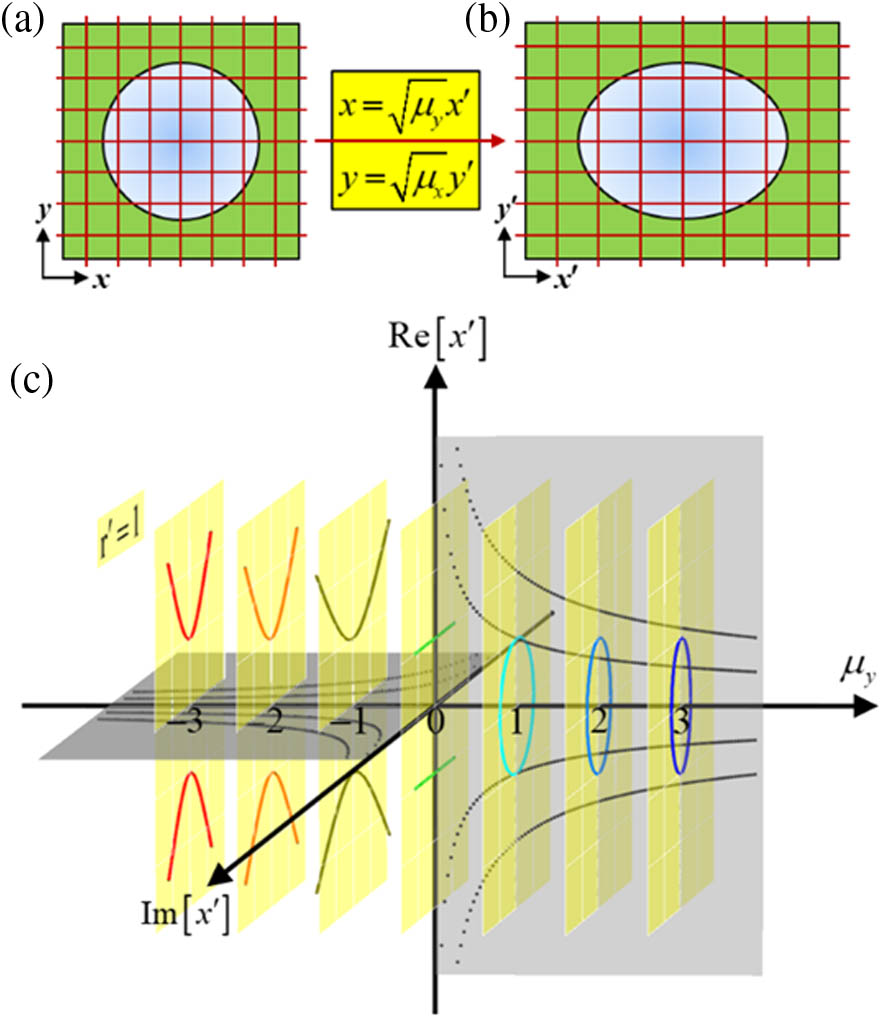
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Institute of Electromagnetics and Acoustics, College of Physical Science and Technology, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117583, Singapore
3 e-mail:
4 e-mail:
Transformation optics (TO) facilitates flexible designs of spatial modulation of optical materials via coordinate transformations, thus, enabling on-demand manipulations of electromagnetic waves. However, the application of TO theory in control of hyperbolic waves remains elusive due to the spatial metric signature transition from () to () of a two-dimensional hyperbolic geometry. Here, we proposed a distinct Pythagorean theorem, which leads to establishing an anisotropic Fermat’s principle. It helps to construct anisotropic geometries and is a powerful tool for manipulating hyperbolic waves at the nanoscale and polaritons. Making use of absolute instruments, the excellent collimating and focusing behaviors of naturally in-plane hyperbolic polaritons in van der Waals layers are demonstrated, which opens up a new way for polaritons manipulation.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(10): B14
1 上海大学通信与信息工程学院, 特种光纤与光接入网重点实验室, 特种光纤与先进通信国际合作联合实验室,上海先进通信与数据科学研究院, 上海 200444
2 上海师范大学天华学院工学院, 上海 201815
提出一种基于纳米膜涂覆的外包层腐蚀双包层光纤(DCF)复合结构传感器。该结构可以通过调控腐蚀时间和纳米膜涂覆厚度来改变传感器的耦合模式、谐振波长、最佳折射率传感区间等传感器参数。理论分析了DCF外包层厚度减小时,DCF模式耦合特性以及折射率传感灵敏度的变化情况。实验中通过在外包层直径为59 μm的DCF上涂覆2000层的Al2O3纳米膜,实现了在1.336~1.356折射率范围内1200 nm/RIU的灵敏度(RIU为单位折射率),这是未经腐蚀和涂覆DCF的24倍。该传感器具有灵敏度高、一致性好、耦合模式可控、传感器参数可定制化等优点,有望在生物医学和化学检测等领域有极大的应用价值。
光纤光学 折射率传感 双包层光纤 腐蚀 纳米膜





